The mandate is clear: modernize your data infrastructure or risk falling behind. Organizations are moving critical analytics workloads from legacy platforms—Informatica, IBM DataStage, Microsoft SSIS, Ab Initio, and aging on-premises databases—to Snowflake’s cloud data platform. The business case is compelling: elastic scalability, lower TCO, and AI-ready infrastructure.
Yet traditional data migration projects have earned their reputation as expensive, time-consuming endeavors. Research from McKinsey finds that 75% of cloud migrations exceed their budgets, with 38% running behind schedule—representing over $100 billion in wasted migration spend globally.
But here’s the new reality: Snowflake data migration in 2025 looks fundamentally different. The emergence of AI-assisted development, modern transformation frameworks, and cloud-native DevOps practices has collapsed timelines from quarters to weeks while improving quality and governance.
This guide provides a strategic roadmap for data engineers, architects, and data leaders planning Snowflake migrations. You’ll learn what to prioritize, which pitfalls to avoid, and how modern tools accelerate time-to-value. This isn’t theory; it’s based on real migrations with real proof points from Coalesce customers that have defied the odds and successfully migrated to Snowflake in weeks, not months or quarters.
Why organizations are migrating to Snowflake
The legacy constraint
Traditional ETL platforms and on-premises data warehouses carry constraints that become more painful as data volumes explode and business expectations accelerate:
Scalability limitations: Legacy systems built on single-server or small-cluster architectures hit hard limits when marketing teams suddenly need to analyze 5 billion customer interactions instead of 500 million.
High TCO: Beyond software licensing fees reaching millions annually, organizations pay for dedicated infrastructure, scarce specialized skills (finding experienced Informatica developers gets harder each year), and maintenance windows that consume weekends.
AI/ML limitations: Legacy platforms weren’t designed for modern AI workloads—training large language models, running real-time recommendation engines, or supporting conversational analytics with generative AI demands computational flexibility these systems cannot provide.
Technical debt accumulation: Years of quick fixes create fragile systems where nobody fully understands the logic. Your best engineers spend time maintaining systems instead of delivering innovation.
What Snowflake enables
Snowflake’s architecture eliminates these constraints:
- Elastic compute and storage separation: Scale compute independently from storage. Spin up a 4XL warehouse for 10 minutes, then shut it down. Storage costs pennies per terabyte monthly.
- Near-unlimited scale: Process petabytes across thousands of concurrent users without complex tuning or infrastructure management.
- Consumption-based pricing: Pay only for compute resources actually consumed, not peak capacity used 10% of the time.
- Cloud-native architecture: Continuous updates, new features quarterly, and security enhancements without months-long upgrade projects.
- Modern ecosystem: Native connectors for BI platforms, reverse ETL tools, and AI/ML frameworks.
| Aspect | Legacy Systems | Snowflake |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Single-server or small-cluster architecture; vertical scaling limits | Multi-cluster shared data; near-unlimited elastic scale |
| Cost Model | CAPEX: Pay for peak capacity used 10% of the time | OPEX: Pay only for compute actually consumed |
| Maintenance | Manual patching, upgrade projects, weekend downtime | Automatic updates, zero downtime, continuous innovation |
| AI/ML Support | Not designed for LLM workloads, vector search, or real-time inference | Native Cortex AI, Snowpark ML, streaming support |
| Skills Required | Specialized, scarce expertise (Informatica, DataStage) | Standard SQL plus modern DevOps practices |
| Integration | Proprietary connectors, brittle connections | Rich ecosystem with native BI, ETL, AI tool integrations |
The AI urgency
AI and large language models have created a step-function change in requirements. Organizations need:
- Massive compute scale for training models
- Low-latency data access for serving predictions
- Vector storage for semantic embeddings
- Real-time streaming pipelines
Legacy systems simply can’t support these patterns. But ironically, the same AI technology creating pressure to modernize also solves the migration challenge—LLMs excel at parsing legacy code and accelerating conversion. Organizations can now “leverage AI to get to AI.”
The core challenges of Snowflake migrations
Understanding what derails migrations helps you avoid common traps:
Timeline pressure vs. quality requirements
Business stakeholders want speed; technical teams need time for validation. This tension creates dangerous dynamics—teams either cut corners (skipping validation) or miss deadlines (losing organizational confidence).
The solution: Adopt methodologies and tools that deliver both speed and correctness. Organizations using modern frameworks routinely migrate priority domains in 4-6 weeks while proving data equivalence through automated validation.
Proving equivalence before cutover
Demonstrating that new pipelines produce results identical to legacy systems is technically challenging. “Acceptably close” gets complicated due to rounding differences, timestamp precision variations, and intentional improvements (fixing legacy bugs).
Validation requires parallel runs, row count comparisons, checksums, referential integrity checks, business rule validation, and distribution analysis. Teams often underestimate this—what seems like a two-week task stretches to six weeks.
Hidden dependencies and complexity
Legacy systems hide complexity behind undocumented tribal knowledge and years of incremental changes:
- Mysterious business rules buried in code with no explanation
- Cross-system dependencies spanning five systems and three teams
- Hardcoded logic scattered across dozens of transformations
- Custom code that doesn’t translate 1:1 to Snowflake SQL
- Circular dependencies requiring careful ordering
The challenge compounds at scale. Migrating 1,000 interdependent objects requires sophisticated dependency mapping and parallel development.
Performance regression risks
Snowflake’s architecture differs fundamentally from traditional databases. Query structures optimized for Oracle might cause full table scans in Snowflake. Clustering keys, micro-partitions, and cost optimization require different strategies. Teams often discover performance issues late—during UAT or post-cutover—requiring costly remediation.
Skills and knowledge gaps
Successful migration requires rare combinations: deep legacy platform expertise + modern cloud-native development + Snowflake-specific knowledge. Finding developers who understand Informatica PowerCenter or Ab Initio—while also knowing Git-based CI/CD, DevOps practices, and Snowflake optimization—is challenging.
Governance and compliance
Moving data to the cloud raises critical questions:
- How do you maintain data lineage through migration?
- How do you ensure PII masking rules transfer correctly?
- Who owns each pipeline and what are SLAs?
- How do you establish audit trails for regulatory compliance?
Organizations that treat governance as afterthought face costly remediation or failed audits.
Technical debt migration
The temptation to lift-and-shift everything perpetuates bad patterns. That seven-layer nested view? Still seven layers in Snowflake. Transformations that recalculate dimensions nightly instead of incrementally? Still inefficient, but now costing cloud credits.
Migration is an opportunity to refactor—but distinguishing “messy but works” from “fundamentally broken” requires both technical judgment and business context.
Cost considerations
Understanding total costs enables realistic planning:
- Snowflake costs: Compute charges (by second, based on warehouse size) and storage (per terabyte-month, plus time travel/fail-safe)
- Migration project costs: Staff time, conversion tool licenses, consulting fees, parallel-run infrastructure
- Hidden costs: Extended timelines, rework when validation issues discovered late, stakeholder confidence erosion
The business case rests on TCO reduction and productivity gains. But realizing those benefits requires successful migration and ongoing optimization—not just moving workloads.
Common Snowflake migration anti-patterns to avoid
Learning from others’ mistakes accelerates your success:
Lift-and-shift without refactoring
The trap: Converting legacy code mechanically without rethinking architecture.
Why it fails: Legacy constraints (limited compute, expensive storage, batch-oriented processing) become liabilities in Snowflake. You pay for cloud infrastructure but realize only a fraction of benefits.
The right approach: Selective refactoring—understand business intent, then implement using Snowflake-native patterns. Focus deep refactoring on the 20% of objects that matter most.
Big-bang cutover
The trap: Migrating everything at once—one weekend, all or nothing.
Why it fails: Concentrated risk. If anything goes wrong, you’re down. Rollback means reverting everything.
The right approach: Domain-by-domain migration. Start with low-risk domains to prove methodology, build confidence, then tackle complex domains. Companies like 1-800-Flowers migrated 88 production pipelines in 4 months by prioritizing incrementally.
Ignoring data quality until production
The trap: Assuming legacy data is clean; deferring quality checks until after migration.
Why it fails: Migration exposes quality issues accumulated over years. Discovering problems post-cutover means stakeholders lose trust.
The right approach: Test-driven migration. Define quality tests before conversion, apply to both legacy and Snowflake outputs in parallel.
Manual code conversion at scale
The trap: Assigning developers to manually rewrite legacy jobs one by one.
Why it fails: It doesn’t scale. Multiply 5-10 objects per developer per week by hundreds of objects, and timelines stretch to quarters. Manual conversion introduces inconsistencies and errors.
The right approach: AI-assisted automation. Modern LLMs parse XML, YAML, SQL and generate Snowflake-native code—compressing weeks of manual work into hours. Organizations report 4-5x productivity improvements.
Skipping validation and reconciliation
The trap: Testing against sample data, then cutting over based on “it looks good.”
Why it fails: Edge cases, data volume effects, and calculation subtleties don’t appear in small test datasets. Post-cutover discrepancies trigger panic.
The right approach: Run legacy and Snowflake pipelines in parallel on production volumes. Compare systematically: row counts, checksums, referential integrity, business rules, distribution analysis. Achieve stakeholder sign-off before cutover.
Migration Red Flags: Warning Signs Your Project Is at Risk
- No written validation plan or sign-off criteria
- Single-person dependencies (“only Jane knows the marketing pipeline”)
- Slipping milestones with vague explanations
- No parallel run budget or timeline
- Stakeholder disagreement on success criteria
- Lack of rollback plan
- Team members expressing private doubts
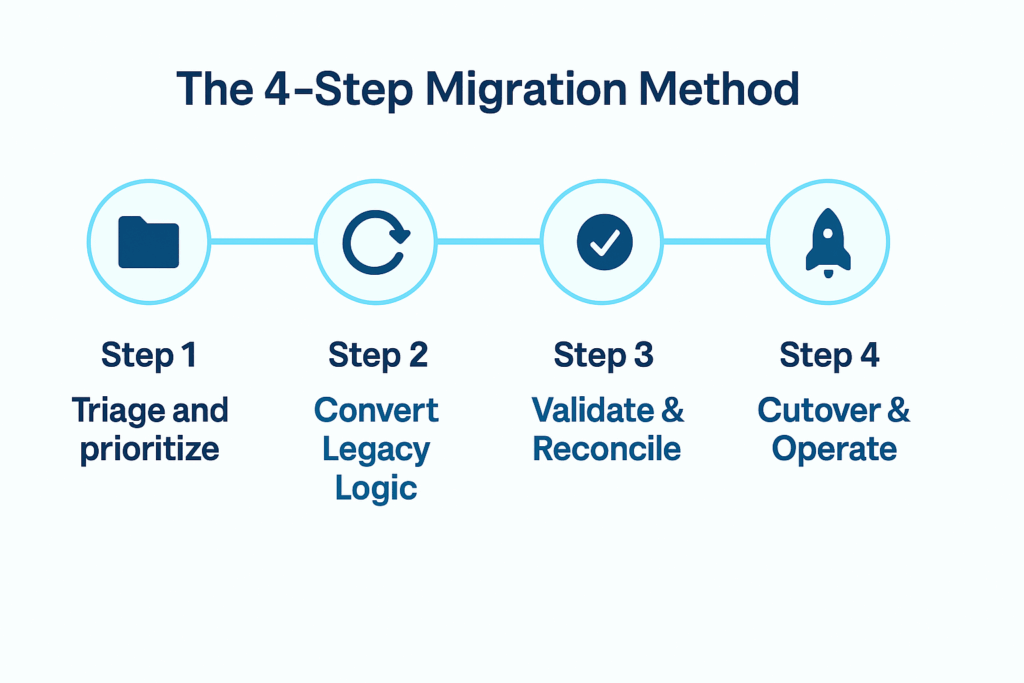
The proven 4-step Snowflake migration methodology
Organizations that succeed follow disciplined methodologies proven across hundreds of projects. This framework, refined through field experience with companies like 1-800-Flowers, N-able (900 objects in 4 weeks), and Q2 (400 objects in 8 weeks), provides a repeatable path from legacy complexity to Snowflake clarity.
Step 1: triage and prioritize
What to do:
– Import legacy metadata and analyze usage patterns
– Map lineage and dependencies
– Identify high-value vs. low-value objects
– Decide what to lift, refactor, or retire
– Define validation criteria and success metrics
Deliverables:
– Inventory and dependency map
– Priority backlog ordered by business value
– Validation plan with sign-off criteria
– Domain owners identified
Time investment: 1-2 weeks. Organizations that invest here accelerate subsequent steps.
Step 2: convert legacy logic to Snowflake
Three conversion approaches:
Manual (simple migrations): Rebuild directly in transformation framework for straightforward logic with few dependencies. Best for small domains (25-50 objects).
AI-assisted (moderate complexity): Use AI copilots to parse legacy code, propose modular designs, and scaffold transformations. Tools like Coalesce Copilot parse Informatica XML, SSIS packages, or custom SQL—generating Snowflake-native implementations in minutes instead of hours.
Bespoke (complex at scale): Partner utilities (Snowflake SnowConvert, Systech DB Shift, NextPathway) automatically translate thousands of objects, then ingest into transformation framework.
Key principle: Standardize during conversion. Use templates for SCDs, naming conventions, audit columns, and error handling. Embed documentation and ownership as you build.
Deliverables:
– Converted pipelines in transformation framework
– Organizational standards applied
– Documentation and lineage captured
Step 3: validate and reconcile
What to do:
– Run legacy and Snowflake pipelines in parallel on production data
– Compare outputs: row counts, checksums, referential integrity, business rules, distributions
– Triage discrepancies (migration bugs vs. legacy issues vs. intentional improvements)
– Achieve stakeholder sign-off domain by domain
Automation is critical: Platforms like Coalesce build testing into workflows—data contracts at node/column level, automated checks, CI/CD gates that block bad deployments.
Deliverables:
– Validation report with test results
– Sign-offs from business stakeholders
– Cutover checklist and rollback plan
Time investment: 2-4 weeks per domain. Don’t rush this—thorough validation prevents post-cutover disasters.
Step 4: cutover and operate
What to do:
– Execute domain-by-domain rollout (not big-bang)
– Use feature flags or time-boxed switches for controlled cutover
– Monitor closely during transition: performance, freshness, errors, downstream impacts
– Establish SLAs/SLOs and quality monitoring
– Plan for post-migration optimization
Success metrics:
– Deployment velocity (1-800-Flowers: 12x faster deployments)
– Refresh time improvements (75% faster nightly batches)
– Data quality scores
– Developer productivity gains
Deliverables:
– Production monitoring dashboards
– Post-cutover review and lessons learned
– Optimization backlog
Sample timeline per domain: Week 0-1 (triage), Week 2-3 (convert), Week 4 (validate), then cutover. Repeat until legacy system retired.
How AI is transforming Snowflake migrations
The emergence of AI has fundamentally altered migration economics and timelines. What took quarters now takes weeks.
What changed
LLMs excel at parsing structured formats: Legacy platforms encode logic in XML (Informatica), JSON, YAML, and proprietary SQL dialects—precisely what transformers-based LLMs trained on code excel at understanding. An Informatica PowerCenter mapping becomes parsed, semantic structure in seconds.
Translation between formats: LLMs generate equivalent logic in target formats. That Informatica mapping becomes Snowflake SQL with appropriate joins, aggregations, and window functions—not mechanical find-and-replace but semantic understanding and regeneration.
Real-world impact:
– Parsing 100 Informatica mappings: Manual (2-3 days) vs. AI (15 minutes)
– Converting ETL jobs to SQL: Manual (4-6 hours per job) vs. AI (5-10 minutes per job)
– Documentation generation: Manual (1 week) vs. AI (1 hour)
Organizations leveraging AI-assisted migration report converting 100-200 objects per week (vs. 20-30 manually)—a 4-5x productivity improvement. Total migration timelines compress from 6-12 months to 2-4 months.
AI Impact: How LLMs Changed the Migration Game
Before AI (2022): Migrating 500 Informatica mappings required 6-9 months of dedicated developer time with manual conversion, inconsistent patterns, and high error rates.
With AI (2025): The same 500 mappings migrate in 6-8 weeks using AI-assisted tools. LLMs parse XML in seconds, generate Snowflake-native SQL, apply consistent patterns, and document automatically.
The transformation isn’t just about speed—it’s about quality. AI-generated code follows best practices, leverages Snowflake-specific features, and embeds governance from the start. Human developers shift from manual coding to reviewing, refining, and validating AI-generated work—a far more strategic use of expertise.
Result: 4-5x productivity improvement while improving code quality and consistency.
AI is both the reason and the enabler
The dual role creates strategic urgency:
Legacy systems can’t support modern AI workloads (training LLMs, real-time recommendations, semantic search). Organizations must migrate to enable AI strategy.
But AI itself makes migration faster. This creates compelling narrative: “We must migrate to Snowflake to enable AI—and we can leverage AI to complete migration 5x faster than traditional approaches.”
Companies like 1-800-Flowers that embraced AI-assisted tools completed migrations in 4 months vs. 12-18 month traditional projections—enabling new analytics capabilities 6-9 months earlier. That’s competitive advantage measured in quarters.
Introducing coalesce: the fast, safe path to Snowflake migration
Organizations routinely migrate hundreds to thousands of objects in weeks using Coalesce, a visual data transformation platform purpose-built for Snowflake.
Why Coalesce accelerates Snowflake migrations
Visual development with code generation: Drag-and-drop interface compiles to optimized Snowflake SQL—no black-box abstraction, full transparency. Templates for SCDs, incremental loads, and error handling accelerate development. New team members ramp faster than with pure SQL.
AI-assisted migration with Copilot: Coalesce Copilot parses legacy XML, YAML, and SQL—proposing modular designs and scaffolding nodes with metadata. This addresses Step 2 (conversion) by compressing days of manual work into hours.
Built-in testing and validation: Data contracts at node/column level enforce schema, freshness, volume, and business rule checks. CI/CD gates block deployments that fail tests. This solves Step 3 (validation) by making quality first-class, not afterthought.
Column-level lineage and impact analysis: See upstream/downstream blast radius before making changes. Understand dependencies during migration planning (Step 1). Impact analysis in pull requests prevents breaking downstream consumers.
Governance by design: Auto-publish ownership, definitions, SLAs to Coalesce Catalog. Audit trails and change tracking for compliance. Quality scores visible to business users. This addresses governance challenge that derails many migrations.
Git-based CI/CD: Version control for all transformations, branch-based development, automated deployments. N-able reduced change implementation time from weeks to days with this capability.
Reusable packages from Marketplace: Pre-built patterns (date dimensions, currency conversion) from Coalesce Marketplace accelerate development without reinventing wheels.
Real customers, real Snowflake migration results
- 88 production pipelines migrated in 4 months
- 1,300 objects, 37,000+ attributes
- 75% faster nightly batches (4-hour rebuild now runs hourly)
- 12x faster deployments
- Git-based version control enabling continuous integration
Q2: 400 objects migrated in just over 2 months
N-able: 900 database objects migrated in 1 month, with regression rates dropping from 70% to near-zero
Denny’s: 25 dimension tables migrated in 3-4 days (60% time reduction vs. legacy process)
| Company | Migration Scope | Timeline | Performance Improvement | Other Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-800-Flowers | 88 pipelines, 1,300 objects | 4 months | 75% faster nightly batches, 12x faster deployments | Git-based CI/CD, hourly data refreshes |
| Q2 | 400 objects | 2 months | Runtime for all jobs reduced by 60% | Rapid migration pace |
| N-able | 900 objects | 1 month | Regression rate: 70% → near-zero | Weeks → days for changes, consistency across environments |
| Denny’s | 25 dimension tables | 3-4 days | 60% time reduction vs. legacy process | Simplified error correction, automated documentation |
Common themes across success stories:
- Speed without chaos (methodical, repeatable approach)
- Quality you can prove (contracts, tests, validation built-in)
- Governed discovery (catalog with ownership and documentation)
- AI-ready foundation (clean, documented models for downstream consumption)
Migration planning essentials
What you bring
- Access to legacy exports/repos and usage data
- Snowflake accounts, roles, warehouses properly configured
- Domain owners who understand business logic
- Stakeholder alignment on priorities and timeline
“It’s just the sheer performance of Coalesce. Our nightly batch processes are 75% faster. We also now have everything in Git, giving us version control and branching. And our deployments are 12x faster.”
— Ed Looft, Data Management & CRM, 1-800-Flowers.com
What Coalesce provides
- Conversion pipeline and proven methodology
- AI-assisted Copilot for acceleration
- Test suites and automated validation
- Catalog documentation and lineage
- Professional services for complex migrations
Sample timeline (per domain)
- Week 0-1: Inventory, triage, validation planning
- Week 2-3: Convert priority jobs, first parallel run
- Week 4: Remediate, UAT, sign-off, cutover
- Repeat until legacy system fully retired
Staffing considerations
- Migration lead/architect (owns methodology)
- Data engineers (legacy expertise + Snowflake skills)
- Business analysts (UAT and validation)
- Data governance/steward (compliance oversight)
Risk mitigation strategies
Hidden dependencies:
– Risk: Downstream systems break after cutover
– Mitigation: Catalog lineage shows blast radius; impact analysis in pull requests
Performance regressions:
– Risk: Snowflake queries slower or more expensive than legacy
– Mitigation: Compiled SQL optimized for Snowflake; monitor credits and query plans; tune clustering/warehouses
Spec drift:
– Risk: Schema changes break consumers
– Mitigation: Data contracts + CI block incompatible changes
People bottlenecks:
– Risk: Only one person knows legacy logic
– Mitigation: Visual design + templates + documentation in Catalog accelerate knowledge transfer
Validation gaps:
– Risk: Discrepancies discovered in production
– Mitigation: Automated parallel runs, parity checks, sign-off gates
Post-migration optimization
Migration establishes functional equivalence—but Snowflake’s value comes from doing things better, faster, cheaper.
Performance tuning priorities
- Query optimization: Profile expensive queries, eliminate full table scans, implement clustering keys on large tables
- Warehouse sizing: Right-size for workload patterns, leverage auto-suspend/resume, use multi-cluster for concurrency
- Materialization strategy: Convert expensive repeated queries to materialized views
Cost management
- Set up resource monitors and alerts
- Analyze query patterns for optimization opportunities
- Review storage optimization (table maintenance, time travel settings)
Continuous improvement
- Monitor quality SLAs/SLOs against baselines
- Gather user feedback on performance and usability
- Iteratively refine based on production patterns
- Leverage new Snowflake features (Snowpark, Cortex, streams/tasks)
Post-migration optimization isn’t “rework”—it’s value realization. Allocate team capacity for ongoing refinement to maximize ROI.
Getting started: next steps
Assessment and readiness
- Inventory your legacy estate (what exists? what’s critical?)
- Identify high-priority domains with clear business value
- Assess team skills and gaps
- Build business case comparing legacy TCO vs. Snowflake value
Pilot approach
- Start with one domain to prove methodology:
- Choose low-risk, moderate-complexity domain
- Execute full 4-step process at small scale
- Measure results (speed, quality, cost)
- Build confidence and refine approach before scaling
Quick Win: Start with a Pilot Domain
Choose a domain that is:
- Low-risk: Not mission-critical to daily operations
- Moderate complexity: Challenging enough to prove methodology, not so complex it overwhelms
- High visibility: Business stakeholders care about results
- Clear ownership: Someone who understands the logic and can validate
Execute the full 4-step process at small scale (4-6 weeks), measure results, and use lessons learned to refine your approach before tackling strategic domains. This builds organizational confidence and de-risks larger migration phases.
Partner considerations
- When to DIY: Simple migrations, SQL-fluent teams, small object counts
- When to engage partners: Complex legacy platforms, thousands of objects, governance requirements, compressed timelines
Coalesce resources
- Ready to accelerate your Snowflake migration? Try Coalesce free for 30 days or schedule a demo and migration assessment.
Snowflake resources
Frequently Asked Questions About Snowflake Migrations
With modern tools and methodologies, priority domains migrate in 4-6 weeks . Complete legacy estate migrations typically take 4-6 months depending on complexity and object count—dramatically faster than the 12-18 months common with traditional approaches. 1-800-Flowers migrated 88 production pipelines in 4 months using Coalesce.
Key factors affecting timeline: legacy platform complexity, data volumes, validation requirements, team experience, and whether you leverage AI-assisted conversion tools.
The top five challenges are:
- Proving equivalence before cutover (validation and reconciliation)
- Hidden dependencies in legacy systems with poor documentation
- Performance optimization (Snowflake requires different tuning strategies)
- Skills gaps (need legacy expertise + Snowflake + modern DevOps)
- Governance continuity (maintaining lineage, ownership, compliance)
Successful migrations address these systematically through disciplined methodology and purpose-built tools rather than hoping issues resolve themselves.
Total cost includes:
- Snowflake infrastructure: Compute (per credit-hour based on warehouse size) and storage (per terabyte-month). Most organizations find Snowflake 30-50% cheaper than legacy TCO within 12-24 months.
- Migration project costs: Internal staff time (or contractor/consultant fees), conversion tool licenses ($50K-$300K for enterprise tools), transformation framework subscriptions.
- Parallel-run costs: Running both legacy and Snowflake systems during validation period (2-4 weeks typically).
ROI timeline: Well-executed migrations pay for themselves within 12-24 months through reduced infrastructure costs, eliminated legacy licensing, and productivity gains. Poor migrations become expensive lessons in cloud cost management.
Yes—Informatica to Snowflake is one of the most common migration paths. Approaches include:
- Automated conversion: Snowflake SnowConvert translates Informatica PowerCenter XML to Snowflake SQL
- AI-assisted rebuild: Tools like Coalesce Copilot parse Informatica mappings and generate Snowflake-native transformations
- Manual rebuild: For simple pipelines, rebuild directly in modern transformation frameworks
Most organizations use hybrid approach: automated conversion for bulk of objects, AI assistance for moderate complexity, manual rebuild for strategic high-value pipelines.
Selective refactoring (often called “lift and shift and improve”):
- Lift as-is: Standard patterns, recent well-designed logic, low-risk simple transformations
- Refactor during migration: Complex nested logic, full refreshes that should be incremental, inefficient patterns costing cloud credits
- Retire: Obsolete assets, unused tables, deprecated processes
Don’t lift-and-shift everything—you’ll pay for cloud infrastructure without realizing benefits. But don’t refactor everything either—perfect is the enemy of done. Apply 80/20 rule: focus deep refactoring on the 20% that drives 80% of value.
Systematic validation approach:
- Parallel runs: Execute legacy and Snowflake pipelines side-by-side on same source data
- Automated checks
- Row count comparisons (must match exactly)
- Numeric checksums (sum of revenue, order counts, etc.)
- Referential integrity (foreign key relationships preserved)
- Business rule validation (derived metrics align)
- Distribution analysis (statistical properties consistent)
- Edge case testing: Null handling, date boundaries, currency conversions
- UAT scenarios: Business stakeholders validate reports and dashboards
- Sign-off: Document validation results, achieve formal approval before cutover
Platforms like Coalesce automate much of this through data contracts, built-in testing, and CI/CD gates—reducing manual validation burden.
Required expertise:
- Legacy platform knowledge: Understanding existing system’s logic and patterns
- Snowflake proficiency: SQL optimization, warehouse sizing, clustering, materialization strategies
- Modern DataOps: Git version control, CI/CD, automated testing, infrastructure-as-code
- Data governance: Lineage tracking, data quality, compliance requirements
Reality check: This rare combination is hard to find in single person. Successful teams either: – Invest in training to upskill existing staff – Hire strategically to fill gaps – Partner with experts (system integrators or specialized consultants) – Leverage tools that reduce skill barriers (visual development, AI assistance, built-in best practices)
Native Snowflake (SQL, stored procedures, tasks):
- Best for: Simple transformations, small teams, organizations prioritizing minimal external dependencies
- Limitations: No visual development, manual documentation, limited reusability, orchestration complexity at scale
Modern transformation frameworks (like Coalesce):
- Best for: Teams wanting productivity gains, organizations requiring governance/documentation, migrations needing consistency and standards
- Advantages: Faster development, automated lineage, built-in testing, collaborative workflows, reusable patterns
Recommendation: Most organizations benefit from transformation frameworks during and after migration. The productivity, governance, and quality improvements justify the investment. Native Snowflake features work well for simple use cases but don’t scale to enterprise complexity.
Code parsing and conversion: LLMs analyze legacy ETL code (XML, YAML, SQL) and generate Snowflake-native implementations—compressing days of manual work into hours.
Documentation generation: AI extracts business logic from code and creates human-readable documentation automatically.
Pattern recognition: AI identifies recurring patterns across legacy estate (SCDs, incremental loads) and suggests standardized implementations.
Optimization recommendations: AI proposes clustering keys, incremental patterns, and performance tuning based on data profiles.
Real impact: Organizations using AI-assisted migration report 4-5x productivity improvements compared to manual approaches. 1-800-Flowers completed migration in 4 months (vs. 12-18 month traditional projection) leveraging AI acceleration.
Prevention strategies:
- Domain-by-domain migration (limits blast radius)
- Thorough validation before cutover
- Documented rollback procedures
- Parallel run safety net (keep legacy active during validation)
If issues arise:
- Minor discrepancies: Use lineage to identify root cause, fix Snowflake code, re-validate
- Major problems: Execute rollback plan (revert to legacy system, investigate, remediate)
- Post-cutover issues: Monitor closely during first weeks, have on-call support, communicate proactively with stakeholders
Risk mitigation through tooling: Platforms like Coalesce reduce failure risk through automated testing, CI/CD gates (bad code can’t deploy), impact analysis (see what breaks before changes ship), and built-in governance.
Domain-by-domain migration is strongly recommended:
- Start with low-risk domain to prove methodology
- Build confidence and refine processes
- Tackle increasingly complex domains
- Maintain legacy system as fallback
Technical implementation:
- Feature flags: Application routes to legacy or Snowflake based on configuration
- Time-boxed switches: Schedule cutover for specific domains at specific times
- Dual-write approach: Temporarily write to both systems during transition
Why this matters: Big-bang cutovers concentrate risk. If anything goes wrong, entire analytics capability is down. Incremental approach allows learning, limits failure blast radius, and provides natural rollback boundaries. 1-800-Flowers migrated 88 pipelines over 4 months this way—proving methodology incrementally.
Lineage preservation strategies:
- Capture legacy lineage: Extract from legacy system metadata, query logs, and code analysis
- Map to Snowflake: Document how legacy objects translate to Snowflake equivalents
- Auto-generate going forward: Use transformation frameworks that automatically track lineage
Tools that help:
- Coalesce : Column-level lineage automatically extracted from transformation logic; visible in Catalog
- Standalone lineage tools: Manta, Informatica, Alation parse SQL and metadata to build lineage graphs
- Manual documentation: Last resort for simple migrations, but doesn’t scale
Why it matters: Auditors, compliance teams, and data stewards need to trace data origin, transformations, and consumers. Losing lineage during migration creates regulatory risk and operational blindness. Build lineage tracking into migration process, not as afterthought.